No products in the cart.
Did you also see the widespread incidents of cervical cancer on your TV and mobile screens? If not, it is crucial to spread awareness of this disease affecting women as it has been one of the most common causes of death for women. The incidence of cervical cancer in India contributes to approximately 6-29% of all cancers in women.
Many of you claim cervical cancer is genetic, so let’s dive deeper into this severe topic and find ways to tackle it together.
What is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical Cancer is developed in the cervix, the body part that connects the vaginal canal to the uterus. Specific gene changes, such as the DICER1 or STK11 gene, may increase the risk of this cancer. There are only a few chances for cervical cancer to be hereditary. Around 70% of cervical cancers take place due to infection with human papillomavirus (HPV).
Furthermore, in rare cases, you may find it hereditary, which means cervical cancer is genetic. A person starts developing cervical cancer or a first-degree relative with cancer due to genetic causes. So, let’s explore the different stages of cervical cancer.
Different Stages Of Cervical Cancer
Staging cancer describes the level of cancer in the body. After a few tests and exams, you can find out the extent of the cancer, like the size of the tumor, which body part has cancer, and where the cancer has spread.
According to FIGO (International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics), the most common staging system for cervical cancer, there are four stages of cancer :
Stage 1A
In this initial stage of cancer when the tumor is in the cervix and is visible only with a microscope. The cancer is around 5mm deep and 7 mm wide.
- Stage 1A1– The tumor is not more than 3mm deep and not more than 7 mm wide.
- Stage 1A2- The tumor is more than 3 mm but less than 5 mm deep and less than 7mm wide.
Stage 1B-
The tumor is in the cervix and is visible without a microscope; even if it’s not, the cancer will be seen with a microscope in a bigger size.
- Stage 1B1- The tumor is smaller than 4 cm in size.
- Stage 1B2– The tumor size is more significant than 4 cm.
Stage 2A
The tumor has been grown beyond the cervix, and the uterus is still not grown into the pelvis walls or the lower vaginal part. The cancer has not spread around the tissue near the cervix and uterus.
- Stage 2A1– The tumor size is not more than 4 cm.
- Stage 2A2- The tumor is more significant than 4 cm at its widest part.
Stage 3A
Tumour has invaded the lower vaginal part but not into the pelvis walls.
Stage 3B
During this stage, the tumor has covered the pelvis walls, resulting in disfunctioning of the kidney from working.
Stage 4A
In the pre-final stage. the tumor is easily visible in the bladder and outside of the pelvis.
Stage 4B
In your final and severe stage, the cancer is spread to many parts of the body, like lymph nodes outside of the pelvis or to the lungs, bone, or liver. It is also known as metastatic cervical cancer.
| Note: Your healthcare provider can only describe the specific staging and treatment plan for cervical cancer |
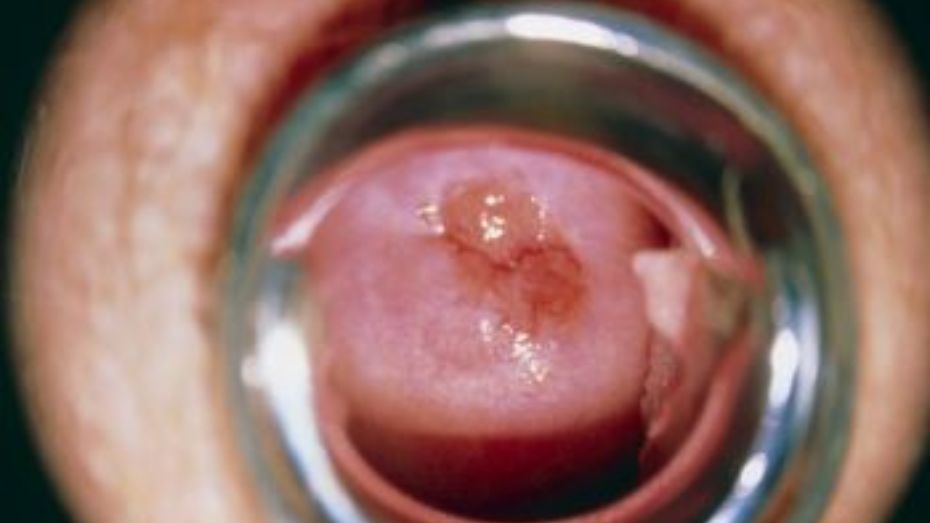
Cervical Cancer Symptoms
You may not notice the signs of this cancer in the early stage because the symptoms generally begin after the cancer has spread.
Early Stage Symptoms
- You may notice vaginal bleeding after having sex or after menopause.
- Sometimes, you may experience heavy periods or longer than usual.
- Watery vaginal discharge and a pungent odor that contains blood.
- It may also cause pelvic pain or pain during sex.
- Also, Cervical cancer is genetic; if your mother had a history of this cancer, your chances of developing this disease may take place.
When cervical cancer has spread beyond the cervix and other body parts, it may include the following symptoms:
- You may have painful bowel movements or rectum bleeding.
- The patient might get Painful urination or urine bleeding.
- Backache, swelling legs, abdomen pain, and fatigue can also be significant signs of cervical cancer.
| Caution: These signs and symptoms can occur in many conditions other than cervical cancer. So, consult your gynecologist for more detailed information. |
Causes of Cervical Cancer
You may not observe why and how cancer develops in your body, but it starts when the healthy cells in the cervix develop changes in their DNA. A cell’s DNA directs the cell to multiply quickly. And the multitude of cells might form a mass, which is a tumor. In addition to that, they can enter and destroy healthy body tissue. These cells, when broken, spread away to other body parts.
“Cervical cancer is genetic.” this statement is not accurate as the maximum cases of cervical cancer are caused by HPV (human papillomavirus). It is a common virus that takes place through sexual contact. It is a prevalent virus that usually goes away on its own. However, the virus brings changes in the cells that lead to cancer.
You Should Not Ignore: Risk Factor for Cervical Cancer
There are several reasons why your condition can get worse:
- Smoking tobacco is one primary reason that can worsen cervical cancer. HPV patient who has a habit of smoking, infections tend to stay for longer periods.
- An increase in the number of your partners will increase the chances of getting HPV.
- Early age sex can enhance the risk of HPV.
- You can also develop cervical cancer if you have a weak immune system and are already suffering from human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Cervical cancer also occurs when you have other sexually transmitted infections.

Keep Cervical Cancer at Bay
Every problem comes with a solution. If you learn to tackle this today, you will have a healthy lifestyle tomorrow. Here are some easy and convenient ways to reduce the risk of cervical cancer:
- The price of cervical cancer vaccine varies on stage, so consult your gynecologist for the proper vaccination.
- The very first step you should follow is to get vaccinated to prevent HPV infection, which might reduce the risk of cervical cancer and other related cancers. Ask your medical doctor about the appropriate vaccine.
- Follow the pathophysiology of cervical cancer as it can detect precancerous conditions of the cervix. The medical organization asks to follow a routine test and repeat it every few years.
- Always remember to have safe sex. Take measures to prevent sexually transmitted infections, meaning using a condom every time you perform sex.
- Everyone knows Smoking is Injurious to health. The people who are addicted to it know its effects go far beyond. People who have yet to try must not.
| Caution: These signs and symptoms can occur in many conditions other than cervical cancer. So, consult your gynecologist for more detailed information.Tip- If you want nursing management of cervical cancer, you may ask your nurse to provide you with the lab results and any abnormal findings, especially about the white and red blood cell counts. |
Wrap Up!
After digging deep, we know that cervical cancer is genetic as well as is mainly spread by human papillomavirus (HPV). It is essential to be aware of this tumor and follow the right path to avoid its symptoms. So, it’s time to prioritize your health and care for yourself. Remember, regular check-ups and screenings are essential. Stay empowered and make your well-being smooth and sound.
Answers to Questions
Q1. What is cervical cancer?
It is a type of cancer that develops in the cervix cells, which is the lower part of your uterus.
Q2. What are the reasons for cervical cancer?
The primary cause of this cancer is the human papillomavirus, a common sexually transmitted infection. Sometimes, cervical cancer is genetic and also involves other factors such as smoking, a weak immune system, and other reasons.
Q3. What are the ways of reducing cervical cancer?
You can decrease the risk of this cancer by getting HPV vaccination, performing safe sex, quitting smoking, and having regular screenings, like PAP tests.
Q4. What are the symptoms of cervical cancer?
In the initial stage, you may observe abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, sexual intercourse pain, and irregular vaginal discharge.
Q5. What is the cervical cancer price?
The price of the cancer vaccine depends on the stage and type of treatment you are pursuing.












